: 26th October, 2023 Applicable for : May, 2024 and subsequent exams till further changes are made. SYLLABUS FINAL PAPER – 1: FINANCIAL REPORTING (100 Marks) Objective (a) To acquire the ability to integrate and solve problems in practical scenarios on Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) for deciding the appropriate accounting treatment and formulating suitable accounting policies. (b) To gain the prowess to recognize and apply disclosure requirements specified in Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) while preparing and presenting the financial statements. (c) To develop the expertise to prepare financial statements of group entities which includes subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements based on Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS). (d) To develop understanding of certain Accounting Standards and solve problems in practical scenarios where treatment is different in both the standards. Contents 1. Section Weightage I 10%-15% Introduction to General Purpose Financial Statements as per Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) Statutory criteria provisions: Applicability Division II of Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013 and Guidance Note thereupon
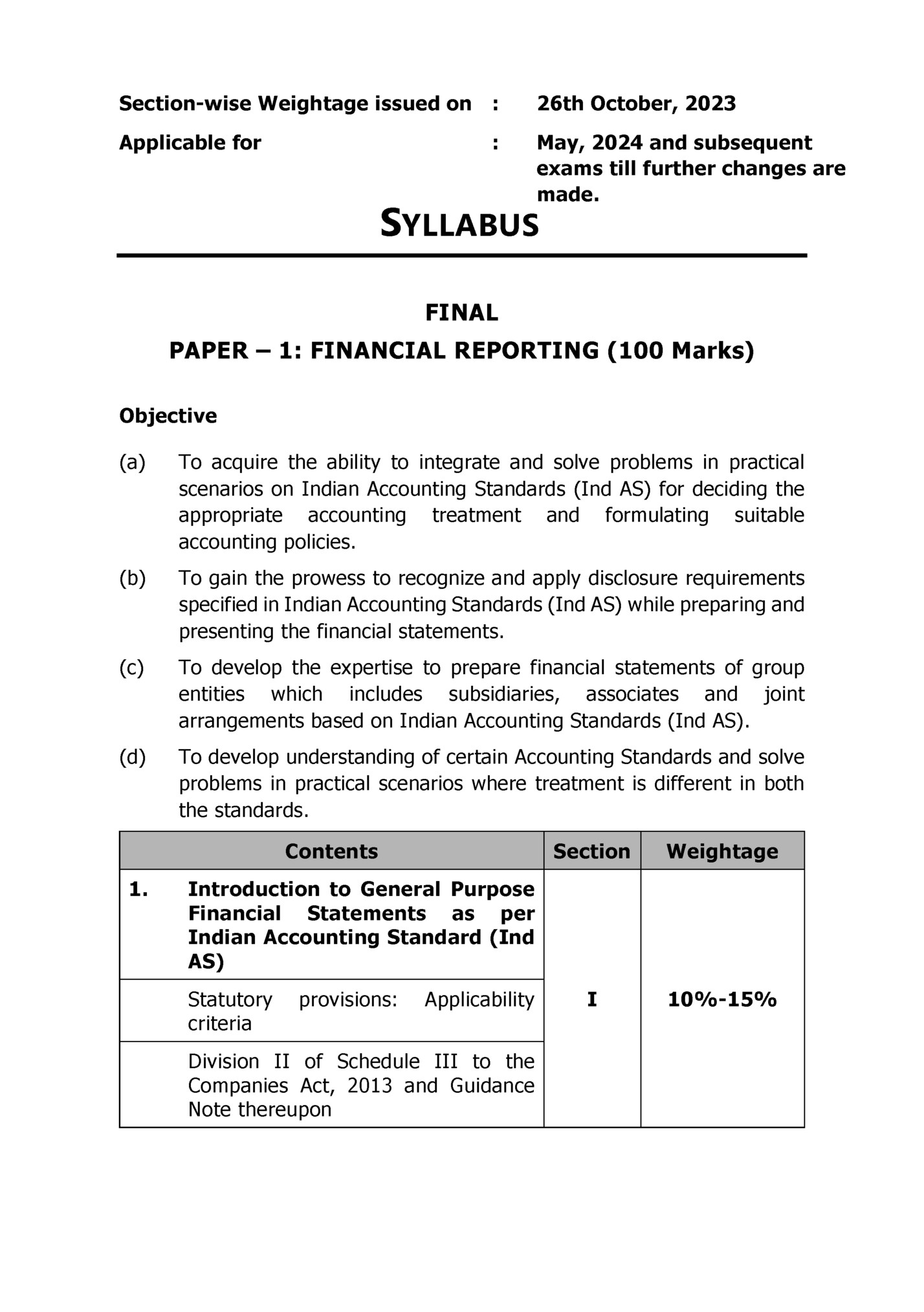
Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting under Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) 3. Application of Ind AS with reference to General Purpose Financial Statements (i) Ind AS on Presentation of Items in the Financial Statements Ind AS 1 “Presentation Financial Statements” of Ind AS 34 “Interim Financial Reporting” Ind AS 7 “Statement of Cash Flows” (ii) Ind AS on Measurement based on Accounting Policies Ind AS 8 “Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors” Ind AS 10 “Events after the Reporting Period” Ind AS 113 Measurement” (iii) “Fair Value Ind AS on Income Statement Ind AS 115* “Revenue from Contracts with the Customers” (iv) Ind AS on Assets and Liabilities of the Financial Statements Ind AS 2 “Inventories” II 5%-10% III 15%-25%
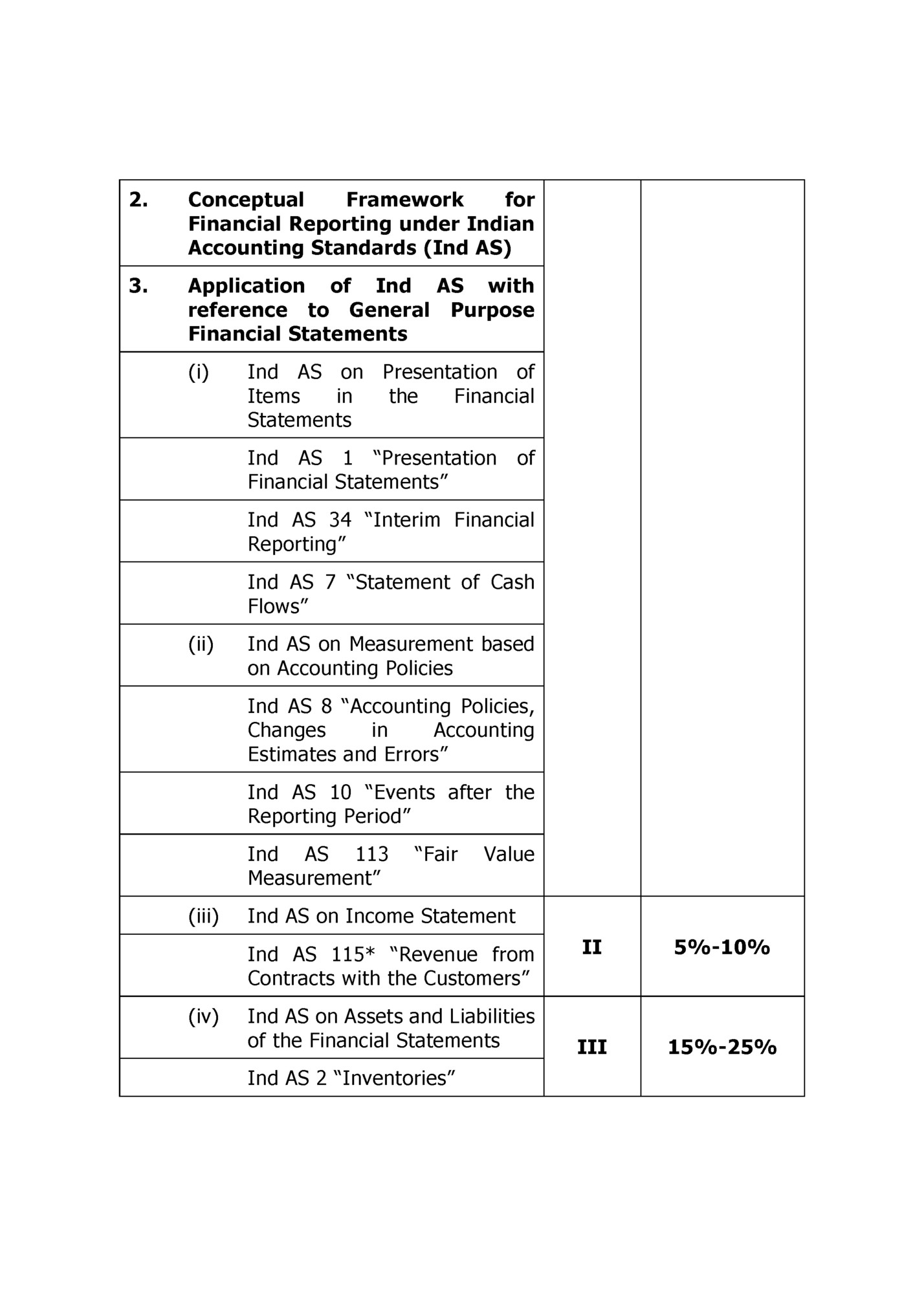
Equipment” Ind AS 116* “Leases” Ind AS 23 “Borrowing Costs” Ind AS 36 “Impairment of Assets” Ind AS 38 “Intangible Assets” Ind AS Property” 40 “Investment Ind AS 105 “Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations” Ind AS 19 “Employee Benefits” Ind AS 37 “Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets” (v) Ind AS on Items impacting the Financial Statements Ind AS 12* “Income Taxes” Ind AS 21 “The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates” (vi) Ind AS on Disclosures in the Financial Statements Ind AS 24 Disclosures” “Related Party Ind AS 33 “Earnings per Share” Ind AS Segments” 108 “Operating IV 15%-20%
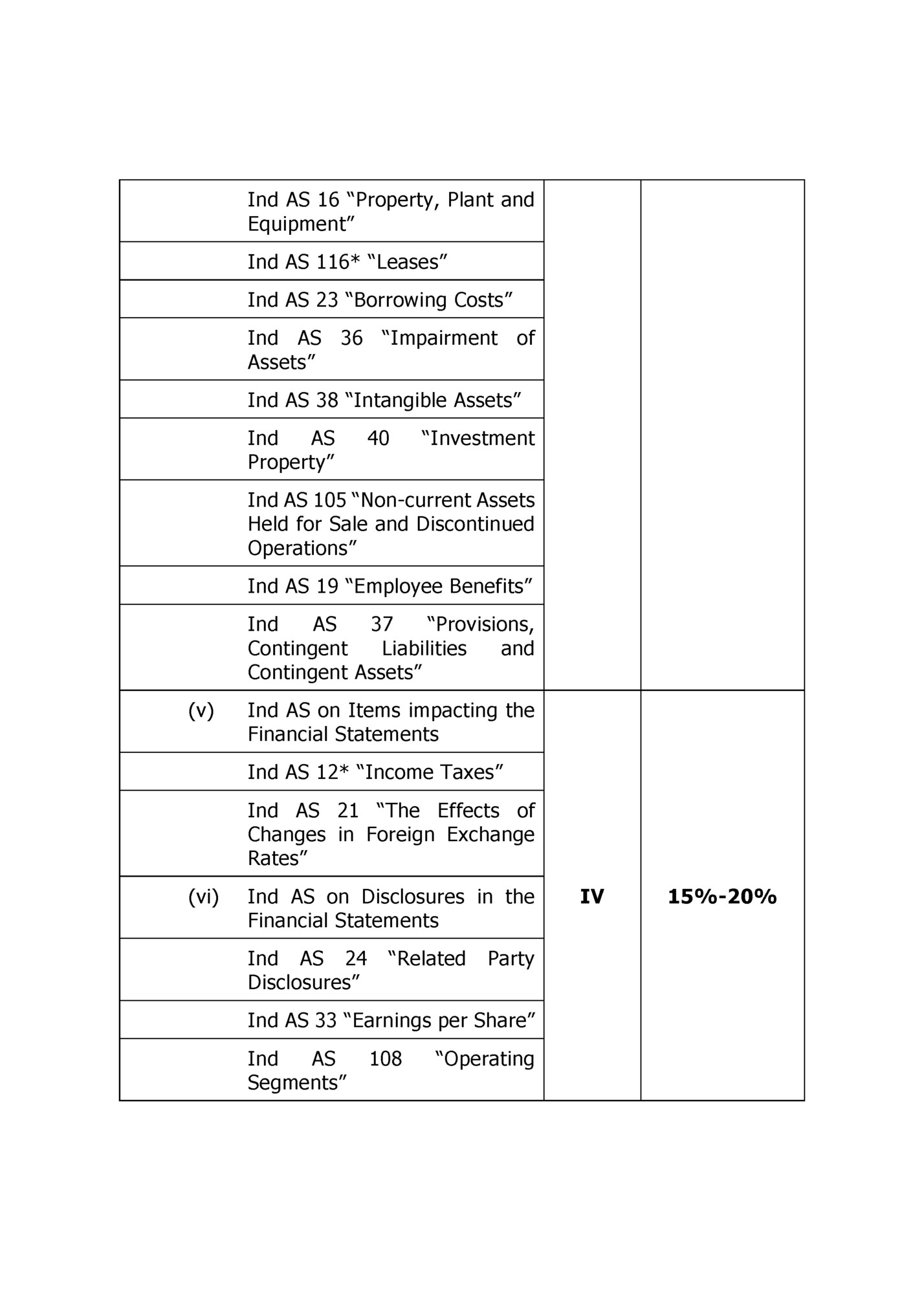
Other Ind AS Ind AS 20 “Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance” Ind AS 102 Payment” “Share Based Ind AS 41 “Agriculture” (viii) Ind AS on Financial Instruments (it includes Ind AS 32, Ind AS 109, Ind AS 107) Financial Instruments: Scope and Definitions Classification and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities Financial Instruments: Equity and Financial Liabilities Derivatives Derivatives and V 10%-15% VI 10%-20% Embedded Recognition and Derecognition of Financial Instruments Hedge Accounting Disclosures 4. Ind AS on Group Accounting (i) Business Combinations (Ind AS 103) (ii) Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements (it
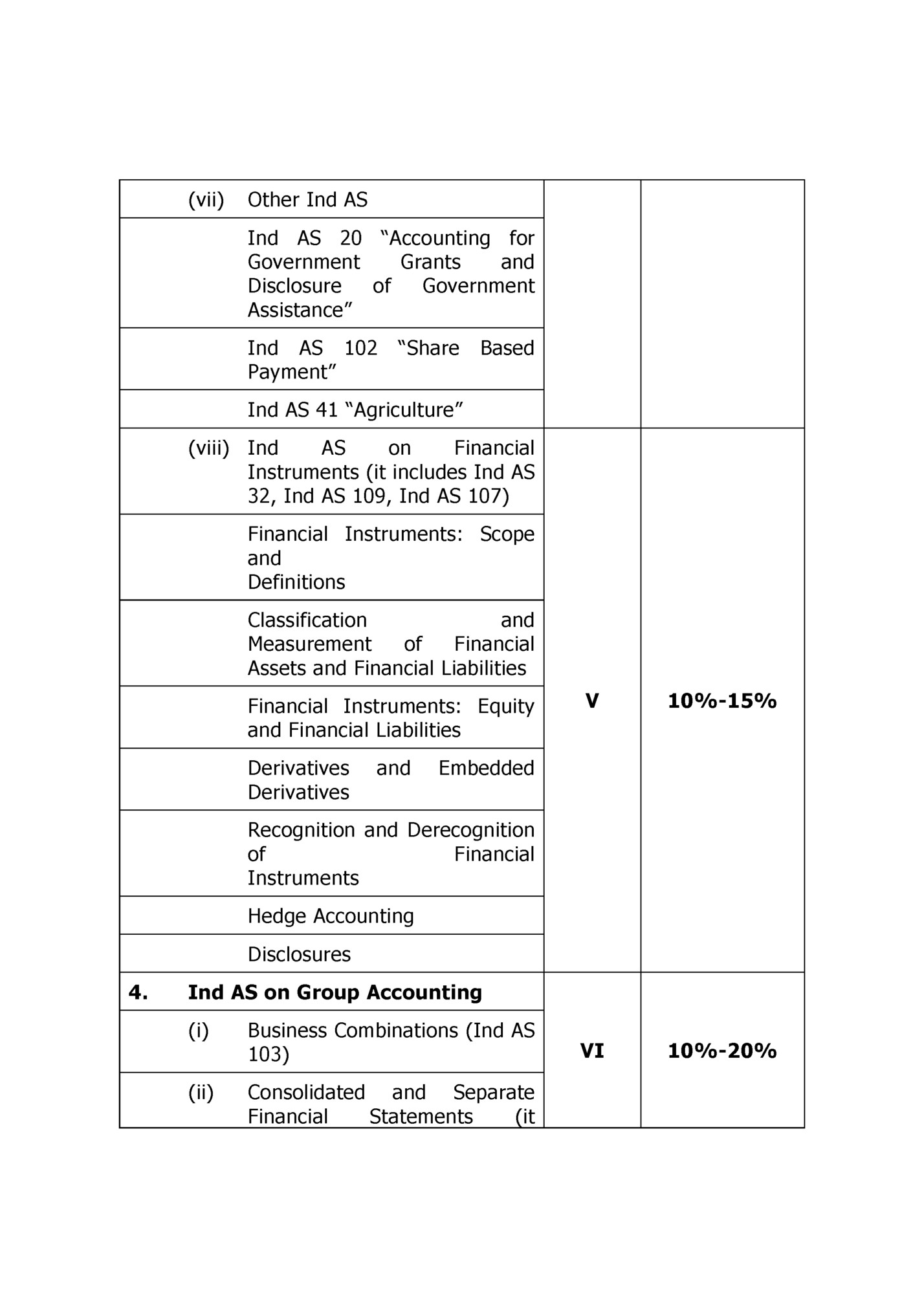
111, Ind AS 27, Ind AS 28, Ind AS 112) 5. First time adoption of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS 101) 6. 5%-10% VIII 5%-10% Analysis of financial statements (as per Ind AS) 7. VII Ethics with Accounting Concepts Identify and explain the key ethical issues 8. Technology and Accounting Evolution of Accounting technological environment in the Notes: 1. *Discussion on AS 7, AS 9, AS 19 and AS 22 will be given along with corresponding Ind AS 115, Ind AS 116 and Ind AS 12. 2. If either a new Ind AS or Announcements and Limited Revisions to Ind AS are issued or the earlier one is withdrawn or new Ind AS, Announcements and Limited Revisions to Ind AS are issued in place of existing Ind AS, the syllabus will accordingly include / exclude such new developments in the place of the existing ones with effect from the date to be notified as decided by the Institute. 3. The specific inclusions / exclusions in any topic covered in the syllabus will be affected every year by way of Study Guidelines.
MANAGEMENT (100 Marks) Objective To acquire the ability to apply financial management theories and techniques in strategic decision making. Contents (1) Risk Management (i) Identification of types of Risk faced by an organisation (ii) Evaluation of Financial Risks (iii) Value at Risk (VAR) (iv) Evaluation of appropriate method for the identification and management of financial risk. Weightage I 8% – 15% Financial Policy and Corporate Strategy (i) Advanced role of CFO in various matters including Value Creation (ii) Strategic decision making framework (ii) Interface of Financial Policy and strategic management (iii) Balancing financial goals vis-à-vis sustainable growth. (2) Section (3) Advanced Capital Budgeting Decisions (i) Current trends in Capital Budgeting ♦ Impact of Inflation on Capital Budgeting Decisions. ♦ Impact of change in technology on Capital Budgeting
of change in Government Policies on Capital Budgeting Dealing with Risk in Investment Decisions Internal and External Factors affecting capital budgeting decision Methods of incorporating risk in Capital Budgeting Adjusted Present Value Optimum Replacement Cycle ♦ (ii) (iii) (iv) (iv) (v) (4) Security Analysis (i) Fundamental Analysis (ii) Technical Analysis - Meaning - Assumptions - Theories and Principles - Charting Techniques - Basics - Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) Analysis (iii) Equity Research and tools available (5) Security Valuation (i) Theory of Valuation (ii) Return Concepts (iii) Equity Risk Premium (iv) Required Return on Equity (v) Discount Rate Selection in Relation to Cash Flows (vi) Approaches to Valuation of Equity Shares (vii) Valuation of Preference Shares (viii) Valuation of Debentures/ Bonds II 20% – 30%
(x) Role and Responsibilities of Valuers Precautions need to be taken by a Valuer before accepting any valuation assignment. (6) Portfolio Management (i) Portfolio Analysis (ii) Portfolio Selection (iii) Capital Market Theory (iv) Portfolio Revision (v) Portfolio Evaluation (vi) Asset Allocation (vii) Fixed Income Portfolio (viii) Risk Analysis of Investment in Distressed Securities (ix) Alternative Investment Avenues - Real Estate - Gold - Private Equity - REITs - Hedge Funds - ETFs - Mutual Funds - Commodities (7) Securitization (i) Introduction (ii) Concept and Definition (iii) Benefits of Securitization (iv) Participants in Securitization (v) Mechanism of Securitization (vi) Problems in Securitization (vii) Securitization Instruments 20% – 30%
of Securitization Instruments (ix) Risks in Securitization (x) Tokenization (xi) Securitization in India (8) Mutual Funds (i) Meaning (ii) Types (iii) Advantages and Disadvantages of Mutual Funds (iv) Evaluation of Mutual Funds (v) Role of Fund Manager in Mutual Funds (vi) Hedge Funds (vii) Role of FIIs in Mutual Funds (9) Derivatives Analysis and Valuation (i) Introduction to Forwards, Futures and Options (ii) Futures Market (iii) Pricing of Forwards and Futures (iv) Hedging using Futures (v) Options (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) - Option Pricing - Option Greeks - Exotic Options Credit Derivatives Real Options Derivative Mishaps and Lessons Swaps Commodity Derivatives Weather Derivatives Electricity Derivatives
Fleepit Digital © 2021